Types of Computers
Computers are integral to the modern world, with applications ranging from everyday personal use to specialized industrial tasks. They come in a variety of shapes and sizes, each designed with specific purposes in mind. This article explores the different types of computers based on their type, size, and purpose, providing a comprehensive overview of the computing landscape.
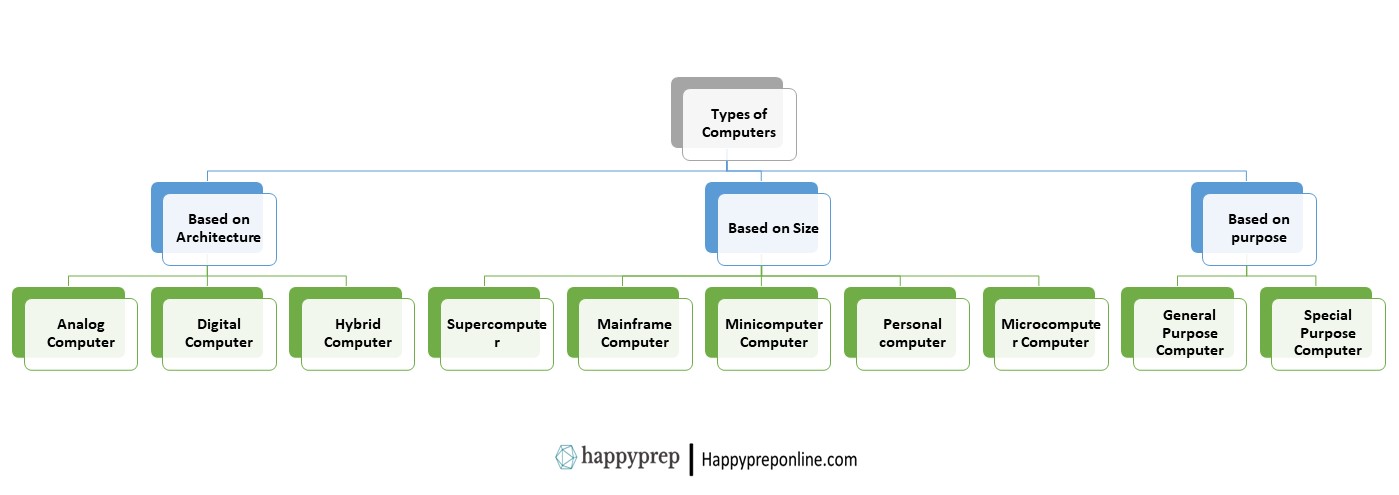
The broad details about the types of computer are explained below:
1. Analog Computers
Analog computers process data by measuring continuous changes in physical quantities like voltage, current, or temperature. These computers are used in applications where continuous data is critical, such as in engineering simulations, scientific experiments, and control systems. Although largely replaced by digital computers, analog technology still has niche applications.
2. Digital Computers
Digital computers work with binary data, performing computations using discrete values (0s and 1s). They are the most common type of computer and encompass a wide range of applications. Digital computers include personal computers, laptops, servers, and mainframes. Their versatility allows them to be used in business, education, entertainment, and many other fields.
3. Hybrid Computers
Hybrid computers combine the features of analog and digital systems. They process both continuous and discrete data, making them ideal for complex simulations and real-time applications. Hybrid computers are commonly used in scientific research, medical equipment, and industrial automation, where they bridge the gap between analog measurement and digital processing.
1. Supercomputers
Supercomputers are the largest and most powerful type of computer, designed for complex computations and data processing at high speeds. They are typically used in scientific research, weather forecasting, simulations, and artificial intelligence. Supercomputers can consist of thousands of interconnected processors working in parallel, allowing them to perform massive calculations quickly.
2. Mainframe Computers
Mainframe computers are large-scale systems used by enterprises and government agencies to manage high-volume transaction processing and large-scale data storage. They are known for their reliability, scalability, and multi-user support. Mainframes are often used in financial services, government operations, and large-scale enterprise computing.
3. Minicomputers
Minicomputers, also known as midrange computers, are smaller than mainframes but more powerful than personal computers. They are used by medium-sized businesses and research institutions for specific applications, such as business operations, manufacturing control, and technical research. Minicomputers offer a balance of performance and affordability.
4. Personal Computers (PCs)
Personal computers are designed for individual use and come in various forms, such as desktops, laptops, and all-in-one systems. They are versatile and can be used for a wide range of purposes, from office work to gaming and content creation. Personal computers are the most common type of computer, making them accessible to a broad audience.
5. Microcomputers
Microcomputers are compact and low-power computers used in embedded systems and consumer electronics. They are often integrated into other devices, providing dedicated functionalities without the need for general-purpose computing. Microcomputers are commonly found in smartphones, tablets, smartwatches, and other portable devices.
1. General-Purpose Computers
General-purpose computers are designed to handle a wide range of tasks and applications. They can run multiple types of software and are used in various environments, from homes to offices to research institutions. Personal computers and laptops are examples of general-purpose computers, as they can perform tasks like word processing, web browsing, gaming, and software development.
2. Special-Purpose Computers
Special-purpose computers are designed to handle the specific tasks and application. The software of such computers are programmed to process certain kind of data and to produce the certain kind of output.