Adverbs in English
Adverbs in English
Introduction
Adverbs are an essential part of the English language. They help us describe how, when, where, and to what extent an action happens. Without adverbs, our sentences would be less detailed and expressive.
For example:
- She sings. (This sentence is correct but lacks detail.)
- She sings beautifully. (Now we know how she sings!)
What is an Adverb?
An adverb is a word that modifies (describes) a verb, an adjective, or another adverb. It provides extra information about an action, quality, or degree.
Examples of Adverbs in Sentences:
- She speaks softly. (Softly modifies the verb speaks and tells how she speaks.)
- The test was very difficult. (Very modifies the adjective difficult and tells to what extent.)
- He ran extremely fast. (Extremely modifies the adverb fast and tells to what degree.)
Types of Adverbs
Adverbs can be divided into different types based on their function in a sentence.
Adverbs of Manner
Adverbs of manner describe how an action is performed.
Examples in Sentences:
- She dances gracefully.
- He speaks fluently.
- They worked carefully on the project.
These adverbs usually come after the verb or after the object.
Adverbs of Place
Adverbs of place describe where an action happens.
Examples in Sentences:
- She looked everywhere for her keys.
- The children are playing outside.
- He sat near the window.
These adverbs never modify adjectives or other adverbs, only verbs.
Adverbs of Time
Adverbs of time describe when an action happens.
Examples in Sentences:
- We will meet tomorrow.
- She arrived early.
- I have seen this movie before.
These adverbs usually come at the beginning or end of a sentence.
Adverbs of Frequency
Adverbs of frequency describe how often something happens.
Common Adverbs of Frequency:
- Always, Usually, Often, Sometimes, Rarely, Never
Examples in Sentences:
- He always wakes up early.
- They sometimes go to the beach.
- She never eats junk food.
These adverbs usually come before the main verb but after “be” verbs (is, am, are, was, were).
Adverbs of Degree
Adverbs of degree describe the intensity or degree of an action, adjective, or another adverb.
Common Adverbs of Degree:
- Very, Too, Quite, Almost, Completely, Extremely, Absolutely
Examples in Sentences:
- The water is too hot.
- He was very tired.
- She almost missed the bus.
These adverbs usually come before the word they modify.
Interrogative Adverbs
Interrogative adverbs are used to ask questions.
Common Interrogative Adverbs:
- How, When, Where, Why
Examples in Sentences:
- How did you solve this problem?
- When will the train arrive?
- Where is your book?
These adverbs always appear at the beginning of a question.
Relative Adverbs
Relative adverbs are used to connect two clauses in a sentence.
Common Relative Adverbs:
- Where, When, Why
Examples in Sentences:
- This is the house where I was born.
- She remembers the day when she won the prize.
- Do you know the reason why he left early?
These adverbs introduce a dependent clause.
Conjunctive Adverbs
Conjunctive adverbs connect two independent clauses and show relationships like cause-effect, contrast, sequence, or comparison.
Common Conjunctive Adverbs:
- However, Therefore, Moreover, Consequently, Nevertheless, Meanwhile, Otherwise, Thus, Hence, Indeed
Examples in Sentences:
- I wanted to go for a walk; however, it started raining.
- She studied hard; therefore, she passed the exam.
- We planned to leave early; nevertheless, we got delayed.
Conjunctive adverbs often require a semicolon (;) before them and a comma (,) after them when connecting two sentences.
Difference between Adverbs & Adjectives
Many students confuse adverbs with adjectives.
Adjective (Describes a noun) | Adverb (Describes a verb, adjective, or another adverb) |
He is a slow runner. | He runs slowly. |
This is a happy child. | She sings happily. |
Summary
Type | Function | Examples |
Adverbs of Manner | Describe how an action happens | She sings beautifully. |
Adverbs of Place | Describe where an action happens | He looked everywhere. |
Adverbs of Time | Describe when an action happens | We met yesterday. |
Adverbs of Frequency | Describe how often something happens | She always arrives early. |
Adverbs of Degree | Describe to what extent something happens | He is very tired. |
Interrogative Adverbs | Ask questions | Where is she going? |
Relative Adverbs | Connect clauses | This is the house where I was born. |
Conjunctive Adverbs | Connect two independent clauses | She was late; therefore, she missed the bus. |
Quick Links
Want to read some more articles?
-
 Shanghai Cooperation Organization (SCO): Origin, Members, Facts, etc for UPSC and other exams
Shanghai Cooperation Organization (SCO): Origin, Members, Facts, etc for UPSC and other exams -
 BRICS: Origin, members and others for UPSC, PSC & other exams
BRICS: Origin, members and others for UPSC, PSC & other exams -
 BIMSTEC for UPSC: Origin, Members & More
BIMSTEC for UPSC: Origin, Members & More -
 General Science for Competitive exams: UPSC, PSC, APFC, EO-AO, SSC, etc
General Science for Competitive exams: UPSC, PSC, APFC, EO-AO, SSC, etc -
 THE TRADE UNIONS ACT, 1926 for UPSC EPFO APFC/EO-AO, ALC, and Other exams
THE TRADE UNIONS ACT, 1926 for UPSC EPFO APFC/EO-AO, ALC, and Other exams -
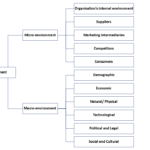 Understanding Macroenvironment: Marketing Environment in Principles of Marketing
Understanding Macroenvironment: Marketing Environment in Principles of Marketing -
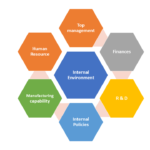 Understanding Microenvironment: Marketing Environment in Principles of Marketing
Understanding Microenvironment: Marketing Environment in Principles of Marketing -
Interjections in English
-
Conjunctions in English
Recruitment notifications update!
-
Recruitment 2025: Recruitment for Teaching Staff in The School of Planning and Architecture, New Delhi - Vacancy, Posts, Grade Pay, etc
-
Recruitment 2025: Vacancies in Inter-University Centre for Astronomy and Astrophysics (IUCAA)
-
Recruitment 2025: Recruitment on Deputation basis in National Anti Doping Agency (NADA)
-
Recruitment 2025: Various vacancies in Artificial Limbs Manufacturing Corporation of India (ALIMCO)
-
Recruitment 2025: Various vacancies in Land Ports Authority of India
Copyright© 2024 | All rights reserved | Made in India